What Is ss Command?
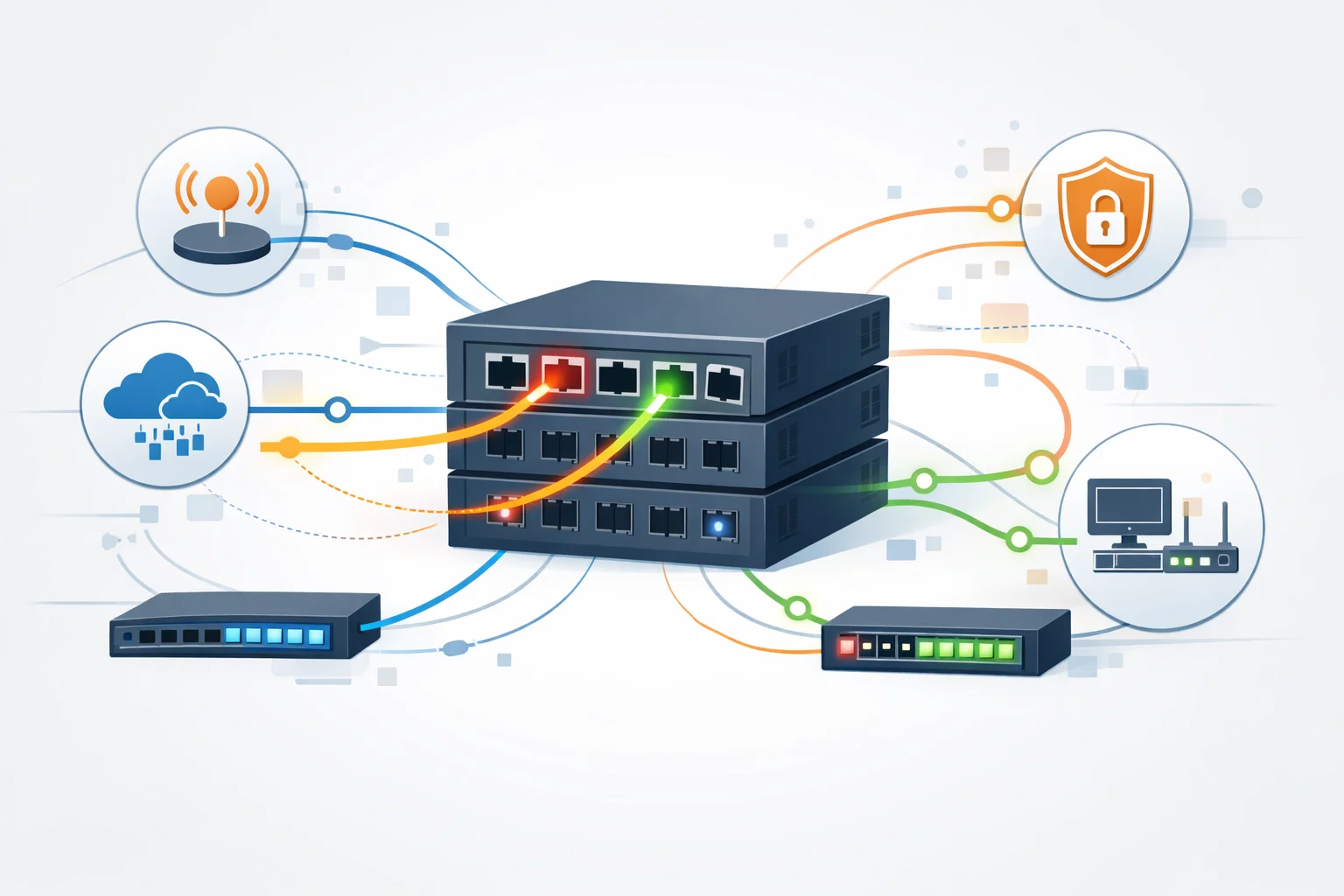
ss (socket statistics) is a modern Linux utility used to display active network connections, listening ports, and socket details.
It is designed as a faster and more informative replacement for netstat.
What Is ss Used For?
- Listing open TCP and UDP ports
- Displaying active connections and states
- Identifying which services listen on which ports
- Analyzing network-related performance or security issues
Basic ss Usage
ss -lnt
Viewing All Active Connections
ss -ant
Listing UDP Ports
ss -lun
Filtering by Port
ss -lnt sport = :80
Including Process Information
ss -lntp
When Should You Use ss?
- Checking if a service port is open
- Testing connectivity after firewall changes
- Investigating suspicious connections
- Troubleshooting network performance
Common Mistakes
- Using netstat instead of ss
- Expecting process info without root privileges
- Confusing IPv4 and IPv6 outputs
Best Practices
- Use ss as the first tool for port issues
- Combine with firewall and service checks
- Monitor connections regularly
- Integrate into monitoring scripts
From a knowledge base perspective, ss is the primary network connection analysis tool on modern Linux systems.