What Is DNS?
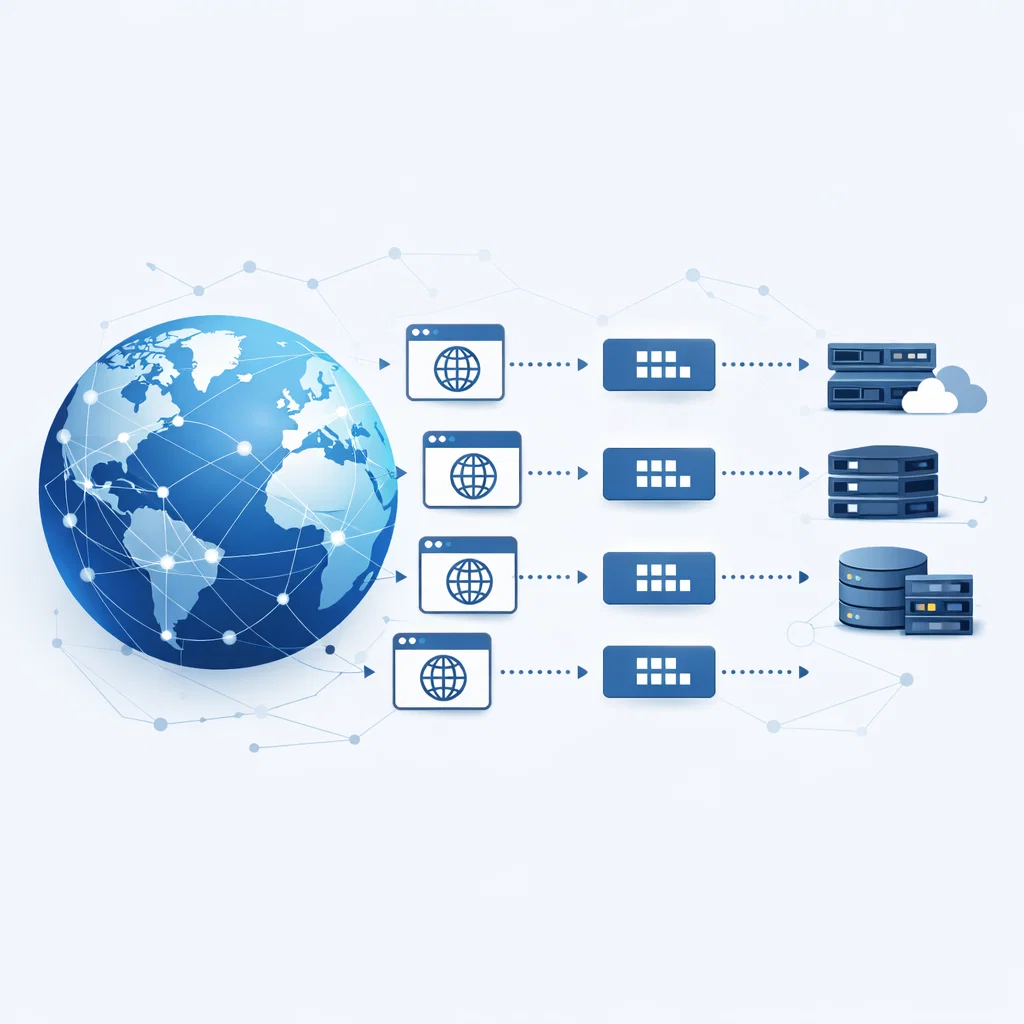
DNS (Domain Name System) is a distributed naming system that translates domain names (e.g., example.com) into IP addresses (e.g., 192.0.2.1).
Without DNS, accessing internet services using human-readable names would not be possible. DNS is a foundational component of network communication.
How Does DNS Resolution Work?
When a domain name is requested, the DNS resolution process follows these steps:
- The client queries the configured DNS server
- The DNS server looks up the IP address
- If found, the IP address is returned to the client
- The client connects to the resolved IP address
Where Are DNS Settings Configured on Linux?
On Linux systems, DNS settings are commonly defined in:
/etc/resolv.conf
Typical entries include:
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 1.1.1.1
search example.local
What Is systemd-resolved?
Modern Linux distributions may use systemd-resolved to manage DNS resolution.
This service provides DNS caching, fallback servers, and interface-based DNS configurations.
DNS Troubleshooting Tools
The following tools are commonly used to diagnose DNS issues:
- dig: Detailed DNS query analysis
- nslookup: Simple DNS queries
- ping: Verifies name-to-IP resolution
Example dig Usage
dig example.com
dig example.com A
dig example.com MX
Common DNS Issues
- Incorrect or unreachable DNS servers
- Cached stale DNS records
- Misconfigured DNS records (A, MX, CNAME)
- Firewall or network restrictions
Best Practices
- Configure multiple DNS servers
- Monitor DNS cache behavior
- Enable logging for critical systems
- Consider TTL values after DNS changes
From a knowledge base perspective, DNS management is a core requirement for network availability and service continuity.